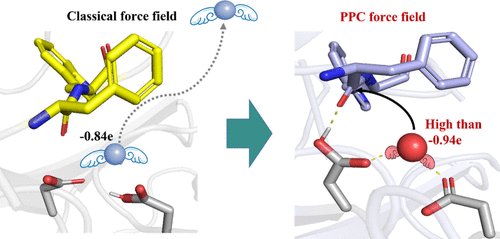
The latest research results of Professor Zhang Lujia's research group at East China Normal University were published in the internationally renowned journal "ACS Catalysis". The article is titled "Aqualigase: A Star Enzyme for One-Step Peptide Bond Dehydration Condensation in a Nature Aqueous Phase". This article shows the latest breakthroughs of the research group in the field of enzyme catalysis, and their graphic abstract was selected as the cover art of the journal, showing the innovative achievements of the research group in the design and application of catalytic enzymes.
Article title: "Aqualigase: A Star Enzyme for One-Step Peptide Bond Dehydration Condensation in a Nature Aqueous Phase"
Journal link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acscatal.5c01532

Research content overview:
This study proposed a new enzyme, Aqualigase, which can achieve dehydration condensation of peptide bonds in a natural aqueous phase through a one-step reaction. This innovative enzyme-catalyzed reaction method breaks through the limitations of traditional chemical methods in aqueous solutions and demonstrates the great potential of Aqualigase in peptide synthesis. Through in-depth research on the enzyme, the research team revealed its catalytic mechanism and demonstrated its application prospects in the synthesis of natural peptides, protein assembly and related biochemical research.
Aqualigase has the unique ability to efficiently catalyze the formation of peptide bonds in aqueous solution. This process is not only efficient and selective, but also can be carried out under mild environmental conditions, avoiding the high temperature or organic solvents required in traditional chemical methods. This technology provides a greener and more environmentally friendly alternative for peptide synthesis, and has a wide range of application potential, especially in the fields of drug development, vaccine development and biomacromolecule synthesis.
The graphic abstract is featured on the cover art
The graphic abstract of this study vividly demonstrates the peptide bond dehydration condensation reaction process of Aqualigase enzyme in natural water phase. Its innovative visual expression was selected as the cover art by the journal "ACS Catalysis", highlighting the green chemical characteristics of the enzyme catalysis and its excellent catalytic performance in aqueous solution.
Research methods and innovations:
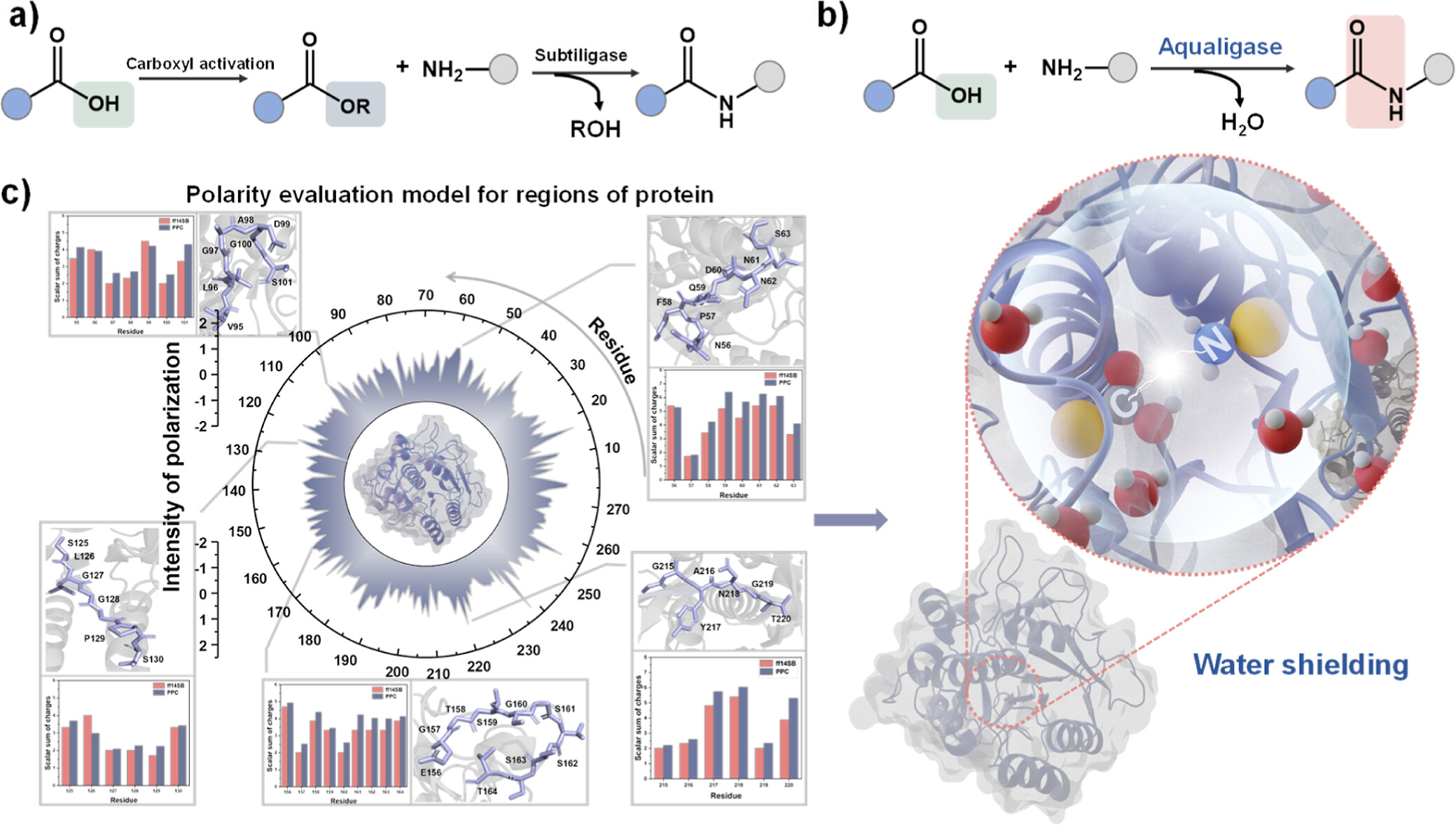
The research team used high-precision molecular dynamics simulation and enzyme structure analysis to deeply study the catalytic mechanism of Aqualigase, and combined with experimental results to prove its ability to efficiently catalyze peptide bond synthesis. This study demonstrated the efficient catalytic performance of Aqualigase in aqueous solution, especially its unique advantages in synthesizing natural peptide molecules. The study also showed that the application of Aqualigase can greatly simplify the peptide synthesis process and improve the selectivity and efficiency of the reaction.
In addition, the research team also verified the application potential of this enzyme in a variety of peptide synthesis reactions through further enzyme catalysis tests and reaction optimization, especially in the development of peptide drugs and vaccines with biomedical application prospects.
Academic and practical significance:
The discovery and development of Aqualigase enzyme has brought revolutionary changes to the field of peptide synthesis. Compared with traditional peptide synthesis methods, Aqualigase provides a more efficient and environmentally friendly synthesis route, especially in reactions in aqueous environments, which provides a new methodology for chemical synthesis and biosynthesis. In addition, the application prospects of this technology in the field of biomedicine are also very broad, especially in vaccine development and protein drug synthesis.
The research results of the research group provide new ideas for the development of catalytic enzymes and make important contributions to the development and application of green chemistry. With the further optimization and application of Aqualigase enzyme, it is expected to become an indispensable and important tool in peptide synthesis and related fields.
Conclusion:
The research results of Zhang Lujia's research group provide a new theoretical basis and practical guidance for the field of enzyme catalyst design and peptide synthesis. By developing Aqualigase, a new enzyme, the research group provides new methods and technologies for green chemistry and sustainable chemistry. The publication of this research result and the cover display of the graphic abstract not only reflect the leading position of East China Normal University in the field of catalytic enzyme research, but also provide valuable experience and technical support for global catalytic enzyme research and application.
The research group will continue to be committed to the research and innovation of catalytic enzymes in the future, promote the application of enzyme catalysis technology in biomedicine and green chemistry, and help achieve sustainable development.